Bridging On-Device and Cloud LLMs for Collaborative Reasoning: A Unified Methodology for Local Routing and Post-Training
Sep 28, 2025·,,,,·
0 min read
Wenzhi Fang
Dong-Jun Han
Liangqi Yuan
Evan Chen
Christopher G. Brinton
Abstract
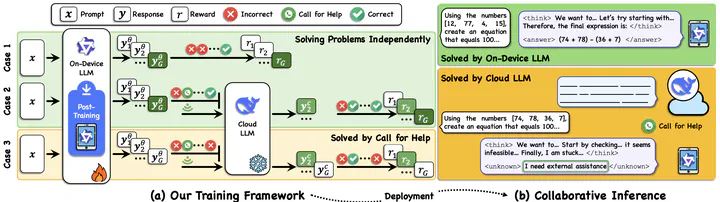
Device-cloud collaboration holds promise for deploying large language models (LLMs), leveraging lightweight on-device models for efficiency while relying on powerful cloud models for superior reasoning. A central challenge in this setting is determining, for each incoming query, whether it should be processed locally or offloaded to the cloud. Existing approaches typically rely on external routers, which often struggle to determine difficulty from the prompt itself, especially for tasks involving complex reasoning. Motivated by this limitation, we propose enabling on-device LLMs to decide internally whether to invoke cloud assistance at inference time, with this capability instilled through reinforcement learning based post-training. Casting on-device LLM post-training as a reward maximization problem, we design hierarchical rewards to encourage local problem solving and judicious cloud offloading. To solve the resulting problem, we develop an algorithm featuring a group-level policy gradient that stabilizes optimization, together with adaptive prompt filtering that provides complementary learning signals to mitigate policy collapse (i.e., exclusive local execution or exclusive cloud offloading). Extensive experiments on on-device-scale LLaMA and Qwen models across multiple reasoning benchmarks show that our method consistently outperforms baselines and significantly narrows the gap to full cloud LLMs.
Type
Publication
arXiv preprint